Build Multicloud Networks for Business Continuity Using Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA)
- Cloud networking , Partners
- June 11, 2021
- RSS Feed
By Henry Wagner, Chief Marketing Officer
Architecting an enterprise multicloud network built for business continuity can be costly and labor-intensive. In this three-part blog series, our team of experts will give you best practices using Oracle Database High Availability features to help.
Originally published in Oracle’s Maximum Availability Architecture Blogs.
No matter what size your business and no matter the industry, planning for unforeseen business interruptions is a must. Customer-impacting outages can result in significant revenue loss, regulatory penalties, and a tarnished brand image.
In the past year, with the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global economy as well as an increase in major cybersecurity incidents such as the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack and the SolarWinds data breach, the importance of business continuity and disaster recovery (DR) have become front-page news.
The key to building a resilient multicloud network as part of your organization’s larger business continuity strategy is planning for and mitigating the impacts that these unplanned disruptions will have on your business. From a networking perspective, business continuity management can be challenging because maintaining network redundancy means you’re often maintaining idle software and hardware resources from multiple vendors, which can get costly. Another challenge is the administrative complexity of managing multiple vendors whose solutions aren’t integrated. This can lead to human error.
In this three-part blog series, our team of experts has put together a set of best practices designed to provide the network redundancy you need based on your business requirements. We’ll cover four different reference architectures that ensure data access, prevent data loss, minimize downtime, and reduce administrative tasks based on varying levels of RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) in the event of an unplanned outage.
Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture
There are four tiers in Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA). The Bronze Architecture, which we will discuss in this blog post, uses a single instance of an Oracle Database. The Silver Architecture, which we will discuss in our next post, as well as in an upcoming webinar on July 13, is designed for high availability (HA), scalability, and fast failover. In the final blog post, we’ll cover the Gold and Platinum Architectures designed for comprehensive High Availability (HA), disaster recovery (DR), and data protection.
With Oracle MAA, you can build a resilient network that will prepare you for the next business continuity incident without shattering your IT budget or creating a lot of extra work for your team.
The reference architectures in this series use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) FastConnect and our partner Megaport, a leading global Network as a Service (NaaS) provider. Here are some terms you’ll see referenced in these multicloud architectures:
OCI Fast Connect
- Region - An OCI region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability Domain - An availability domain is one or more data centers located within a region. Availability domains are isolated from each other, fault tolerant, and very unlikely to fail simultaneously.
- Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) - A VCN is a virtual, private network that you set up in Oracle data centers. It closely resembles a traditional network, with firewall rules and specific types of communication gateways that you can choose to use. A VCN resides in a single OCI region.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG) - The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another OCI region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- FastConnect - OCI FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and OCI. FastConnect provides higher bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
Megaport
- Software Defined Network (SDN) - Megaport’s on-demand, global Software Defined Network (SDN) enables fast, flexible, and secure connectivity to the world’s top cloud providers, including Oracle Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, across 700+ locations in North America, Asia-Pacific, and Europe.
- Port - A Port is a high-speed Ethernet interface (1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 100 Gbps) that connects to the Megaport SDN.
- Virtual Cross Connect (VXC) - With a Port configured, you can create Virtual Cross Connects (VXC) to connect to Oracle services on the Megaport network. A VXC is a private point-to-point Ethernet connection between an A-End (your Port) and a B-End (for example, OCI FastConnect).
Let’s review how the Bronze tier in Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture works with Megaport’s services.
Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture - Bronze Architecture
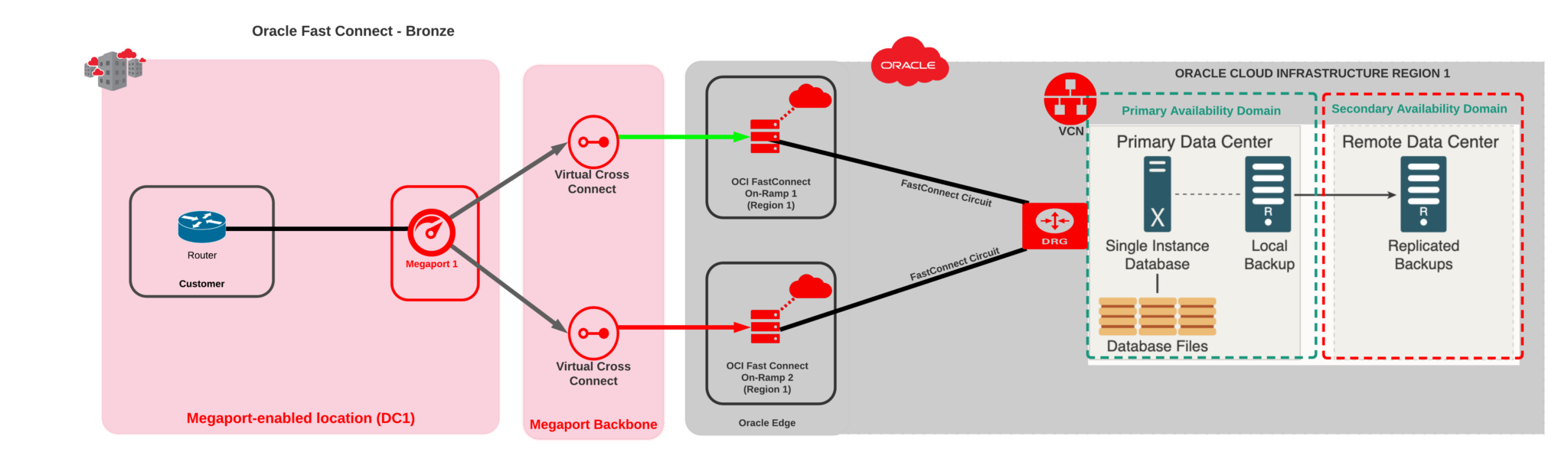
Oracle MAA Bronze Architecture using Megaport
The Oracle MAA Bronze Architecture provides a basic database service with automated backup at the lowest possible cost. This architecture is best used for databases deployed in development & test environments, and for non-mission-critical production databases. In the example in the diagram above, the architecture spans multiple cloud platforms with the application tier being located on another cloud platform or on-premises while the Oracle Database (i.e. Autonomous Database Service) runs in OCI.
One of the key questions you should ask your business when deciding whether to use this architecture is: How much downtime can your customer afford?
In the Bronze Architecture, you would deploy a Megaport Port at your data center location and create two VXCs–one primary and one backup–to get on Megaport’s private, fully redundant network, which will connect to Oracle’s redundant routers at the OCI FastConnect location.
Each virtual connection will be a standalone Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session between your on-premises resources and your Oracle Databases in OCI.
This simple architecture creates redundancy for your database and provides data protection at an affordable cost with automated backup and recovery built into the Autonomous Database and other Oracle database cloud services.
Next time
We’ll cover the Oracle MAA Silver Architecture, designed for databases that can’t afford to wait for a cold restart or a restore from backup should there be an unrecoverable database instance or server failure.



