SD-WAN and MPLS: Weighing the Similarities, Differences, and Benefits
- Cloud networking
- April 7, 2025
- RSS Feed
By Mark Austen, Solutions Architect
Compare these two leading networking technologies so you can decide which is best for your organization.
In 2025, Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) is considered an essential part of many organizations’ network fabric. But what about Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)? Has this trusty routing technique been made redundant by the increasing uptake of SD-WAN? What are the differences and similarities between SD-WAN and MPLS? And are there valid reasons to use both?
In this article we’ll explore both technologies so you can decide which is best for your organization. Let’s start by examining the foundations of SD-WAN and MPLS, and how they work.
What is SD-WAN?
Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) is as it sounds: a software-defined approach toward wide area networking. This approach is ideal for organizations seeking more diversity and control over their enterprise WAN, offering Local Area Network (LAN)-like features at a broader scale.
SD-WAN uses a traditional hardware-based networking model and adds a software-defined virtual network overlay on top. This overlay is managed and provisioned centrally by a controller, so users don’t need to manually configure and manage every device. The underlay, or data plane, is then left with the responsibility to process and transit packets between devices.
The overlay can run over a range of standard network transport services, including the public internet, 4G, 5G, and MPLS. Application-aware routing will assess the performance of underlying network transport to control where and when an application uses a specific service, making sure real-time and sensitive applications run as reliably as possible.
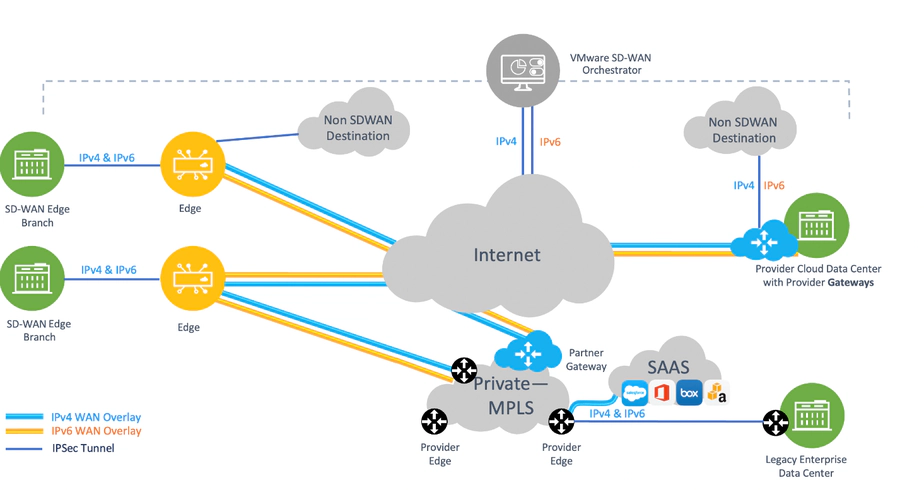
What is MPLS?
Multiprotocol Label Switching is just that—a label-switched-path network model—in which data packets take a pre-defined, private route straight to their destination. This routing takes place over Layer 2 Ethernet or Layer 3 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
MPLS circuits are segregated from the internet and from other MPLS circuits on the carrier’s network, and can instead be viewed as dedicated services bound by their own Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for packet loss, jitter, and latency.
Discover more ways to interconnect your network and supercharge your business operations.
Benefits of SD-WAN
SD-WAN is the newer, and arguably more popular, player in town. Cisco, Fortinet, Aruba, Viptela, Versa, Palo Alto, and Broadcom are the major networking giants that offer SD-WAN solutions to simplify remote and complex enterprise networks. SD-WAN provides its users with a range of benefits.
Centralized management system
Most SD-WAN solutions provide a centralized management system by default, with built-in automation, security, and application-level visibility. This removes the need to integrate SD-WAN devices into another vendor’s network management system, saving significant time and cost.
Flexible private overlay
SD-WAN can build a private overlay over any network transport type, whether it be public internet, private MPLS, or a combination of both. By bundling different types of network transport within this flexible model, users can achieve higher bandwidth at a lower overall cost with improved security.
Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP)
Zero Touch Provisioning, or ZTP, refers to the ability to provision a device or network without the need for local configuration. Some SD-WAN devices support ZTP, meaning they can be shipped to site directly from the factory without the need to apply configurations.
When connected to the internet, a ZTP device will securely connect back to a centralized controller, receive verification against its serial number, download its configuration, and join the overlay network – it’s that simple.
Compare SD-WAN vendors to pick the perfect provider for your use case.
Benefits of MPLS
MPLS is the legacy technology in this comparison, and while its higher price tag and lower flexibility places it at a comparative disadvantage against SD-WAN, it shouldn’t be dismissed; MPLS has its own set of benefits.
Consistent connectivity
MPLS connections can be used as a dedicated private service with SLAs for throughput, latency, and jitter. End-to-end connectivity across an MPLS network is assured by the network operator to perform within the bounds of this SLA, ensuring reliability and consistency.
Proactive network management
MPLS network capacity is proactively managed and end-to-end latency closely monitored by the provider, to ensure paths are clear of congestion and faults are addressed as soon as they occur. This attentive approach to network management minimizes downtime and keeps your teams productive.
Easy deployment
WAN designs with static and predictable requirements can be easily deployed with MPLS. An MPLS-enabled site with a simple redundant design of two MPLS links is easy to both implement and support.
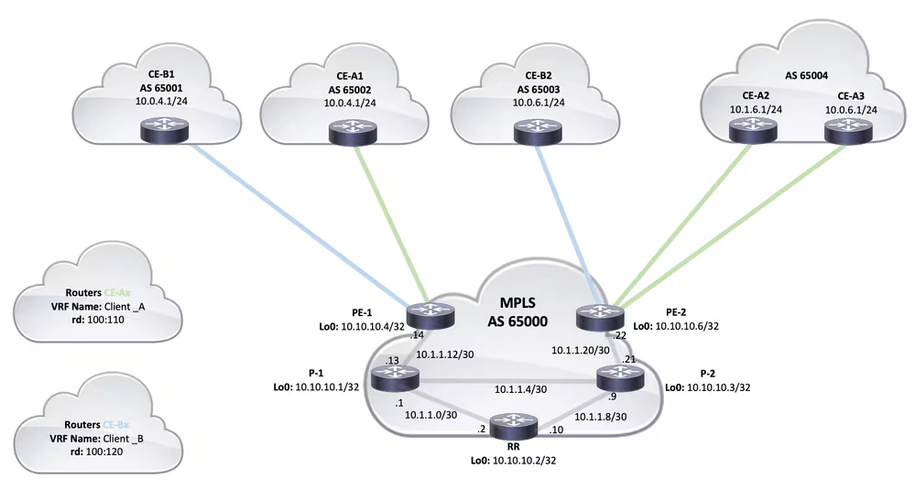
The similarities between SD-WAN and MPLS
While SD-WAN and MPLS have some key differences, they also share some important similarities.
SD-WAN and MPLS both:
- deliver high-performance, reliable, and private WAN connectivity
- provide a type of private overlay – SD-WAN with the use of Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) VPNs, MPLS with labels
- use private IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) addressing to communicate between devices connected to the WAN within their private overlays
- support classification of network traffic into different priority and importance levels.
The verdict
SD-WAN and MPLS are often treated as separate network models, but as our comparison shows, they aren’t directly competing configurations; you don’t have to face an ultimatum between which model is right for you.
If you need to streamline connectivity between multiple endpoints and cloud providers, SD-WAN is a proven, cost-effective solution. If consistency and simplicity is what you’re after, MPLS alone may be your preferred option.
But if you have more complex networking requirements, you can actually use MPLS together with SD-WAN to build a hybrid WAN design.
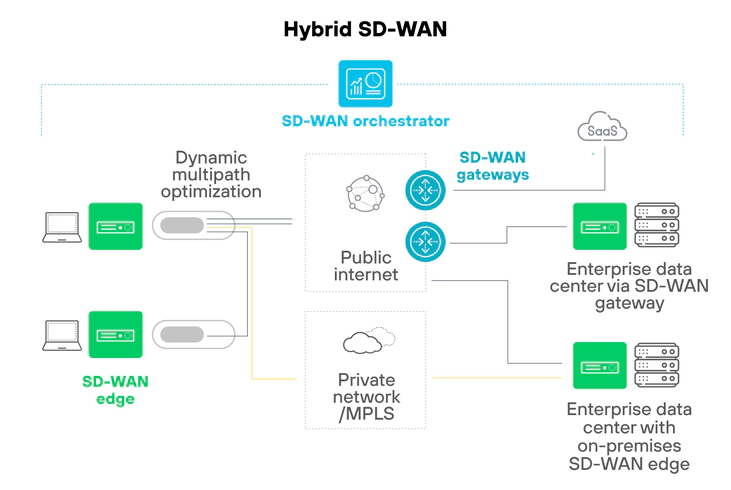
The application-aware routing of SD-WAN ensures critical traffic like Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is directed over your reliable MPLS transport, while non-critical traffic is directed over internet transport. Using MPLS and SD-WAN together is a great way to lay a flexible foundation as your cloud connectivity needs continue to grow and evolve.